Core i7-4770K: Haswell's Performance, Previewed
A recent trip got us access to an early sample of Intel’s upcoming Core i7-4770K. We compare its performance to Ivy Bridge- and Sandy Bridge-based processors, so you have some idea what to expect when Intel officially introduces its Haswell architecture.
Results: OpenCL Performance
Intel enabled OpenCL 1.1 support on its Ivy Bridge-based processors with HD Graphics 4000 and 2500, giving developers an option to exploit the graphics component’s execution units for general-purpose workloads. Popular desktop applications like WinZip and Photoshop now offer sometimes-substantial performance gains on platforms able to more granularly parallelize workloads that would have previously been handled by fewer processing cores. With Haswell, support is being expanded to OpenCL 1.2.
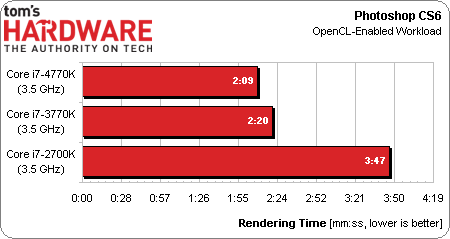
Our Photoshop CS6 benchmark is most effective at showing the difference between processors that lack OpenCL support and those with it. The Core i7-2700K tackles this workload using its four Hyper-Threaded cores, while the -3770K and -4770K get their HD Graphics components involved.
The Haswell-based Core i7-4770K is slightly faster than its predecessor, likely due to a combination of additional EUs, more bandwidth, and higher IPC.
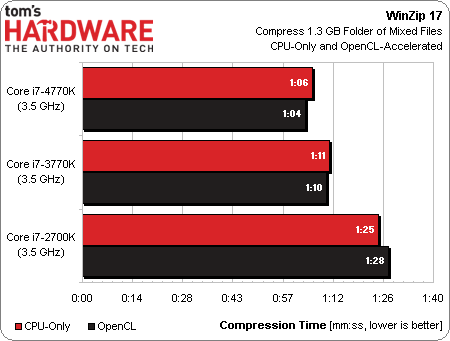
We run our WinZip test with and without OpenCL enabled on all processors, and you can clearly see there isn’t as much differentiation as there was in Photoshop. The explanation is easy enough, though. WinZip 17 is really well-threaded (much more so than 16.5 was). So, the CPU cores are taxed, even without OpenCL support. With OpenCL turned on, WinZip only offloads compression for files larger than 8 MB. So, if our 1.3 GB folder of files is full of documents, PowerPoint presentations, PDFs, and music (which it is), acceleration isn’t going to help much.
We do observe small speed-ups from the Core i7-4770K and -3770K, whereas the -2700K actually slows down when we try turning OpenCL on. The moral of the story? OpenCL is only going to register as a benefit insofar as the tasks you run are well-suited to heterogeneous computing. The Photoshop benchmark represents one end of that spectrum, and our WinZip test illustrates the other.
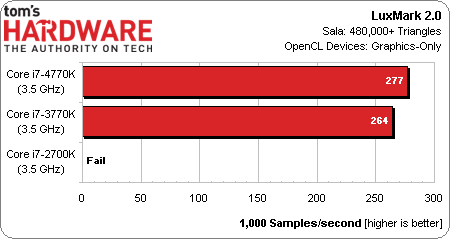
LuxMark 2.0 quantifies the speed-up from HD Graphics 4000 to 4600, simultaneously reminding us that the Core i7-2700K, for as capable as it is, doesn’t help in OpenCL-enabled software. As a side note, AMD's A10-5800K registered 225,000 samples per second, less than the Core i7-3770K.
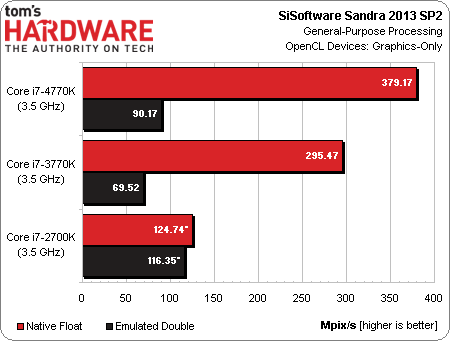
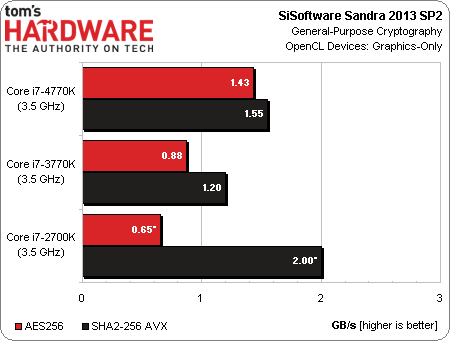
Now, with that said, is OpenCL always going to be the performance win that each of our tests seems to show? Not necessarily. As we see in Sandra 2013’s GP Processing module, FP32 math is significantly faster on Intel’s HD Graphics engine than its x86 cores. However, doubles have to be emulated on all three processors, and the Sandy Bridge-based Core i7-2700K turns in better results there. It turns out that Intel’s powerful x86 cores emulate those results faster than Ivy Bridge or Haswell can on the GPU.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Results: OpenCL Performance
Prev Page Results: Sandra 2013 Next Page Results: Performance Teaser, Per-Clock Perf And Threaded Apps-
twelve25 Obviously with AMD striggling, Intel has no need to really stretch here. This is another simple incremental upgrade. Good jump from socket 1156, but I doubt many 1155 owners will feel the need to buy a new motherboard for this.Reply -
EzioAs Thanks for the preview!Reply
So all of these results are what most people expected already: minimal increase in CPU performance while the iGPU shows significant increase? I'm not surprised really (and I believe most people have speculated this), since Haswell mostly targets the mobile segment.
@twelve25
In my opinion though, unless LGA1156 i5/i7 users really want to upgrade (native USB 3.0, more SATA 3, etc), they can still hold out with their current CPUs. Although upgrading to Haswell rather than IB does make much more sense if they really want to but there's also the reported USB 3.0 bug and we haven't seen the thermals and overclocking capability on this chip so it might actually be a turn off for some people. And yeah, I don't think many SB or IB users will upgrade to Haswell. -
dagamer34 @twelve25 But who does Intel really need to convince here? Trying to chase after people who upgrade every year is a fools errand because its such a small piece of the pie compared to the overall larger market. Besides, most of Intel's resources are clearly going towards making mobile chips better, where there energy really needs to be anyway.Reply -
dagamer34 To add to EzioAs's point, I don't see most people on SB/IVB systems upgrading until Intel makes chips that have a good 10-15% better performance than 4.2-4.5Ghz SB/IVB systems or they decide to go down the APU route like AMD is (and also find/create workloads which an APU would beat those systems). In other words, not for another 2+ years.Reply -
Adroid killerchickensDoes Haswell run hot as Ivy Bridge?That = the million dollar question. Did they do away with the bird poop and return to fluxless solder.Reply
Intel should stop throwing insults to the overclocking crowd. We will pay another 10$ for the fluxless solder. -
mayankleoboy1 @ Chris Angelini : Man, you are amazing for this preview! +1 to Toms.Reply
There is no surprise at Intel excluding TSX from the unlocked K parts. They removed teh VT-d in the Sb/IB too. Just so that people not use teh $300 chip in servers, but have to buy th e$2000 chip.
Intel are fucked up
i dont think Intel will be too happy with Toms for this preview.... -
sixdegree Good preview. I kinda hoped that Toms includes the power consumption figure for Haswell. It's the biggest selling point of Haswell, after all.Reply -
mayankleoboy1 sixdegreeGood preview. I kinda hoped that Toms includes the power consumption figure for Haswell. It's the biggest selling point of Haswell, after all.Reply
Power consumptions is a lot dependent on the BIOS optimizations, which are far from final.