SiBEAM Snap And WiGig Wave Goodbye To Physical Connectors
An outgrowth of a research project at the University of California, Berkeley investigating millimeter wave data transmission, SiBEAM, now a wholly-owned subsidiary of Silicon Image, has created a technology that could help eliminate physical connectors from smartphones, tablets, cameras, laptops or any device whose design is constrained by the physical size of peripheral connectors.

SiBEAM Snap wireless connector technology operates in the same 60 GHz frequency band as WiGig, but it operates at a lower power and over much shorter distances. With only a 1 cm range, it can be used to create a wireless docking station. Although the technology is protocol agnostic, its first application implements USB 3.0, offering 12 Gb/s aggregate (6 Gb/s full-duplex) throughput.
The SB6212 Snap transmitter and SB6213 Snap receiver ICs are approximately 4x6 mm in size and don't require an external antenna; the antennae are embedded within the chips. Snap also doesn't require any additional software drivers because they integrate with existing bus technology. While USB is SiBEAM's first target, Snap could also handle HDMI or DisplayPort traffic.
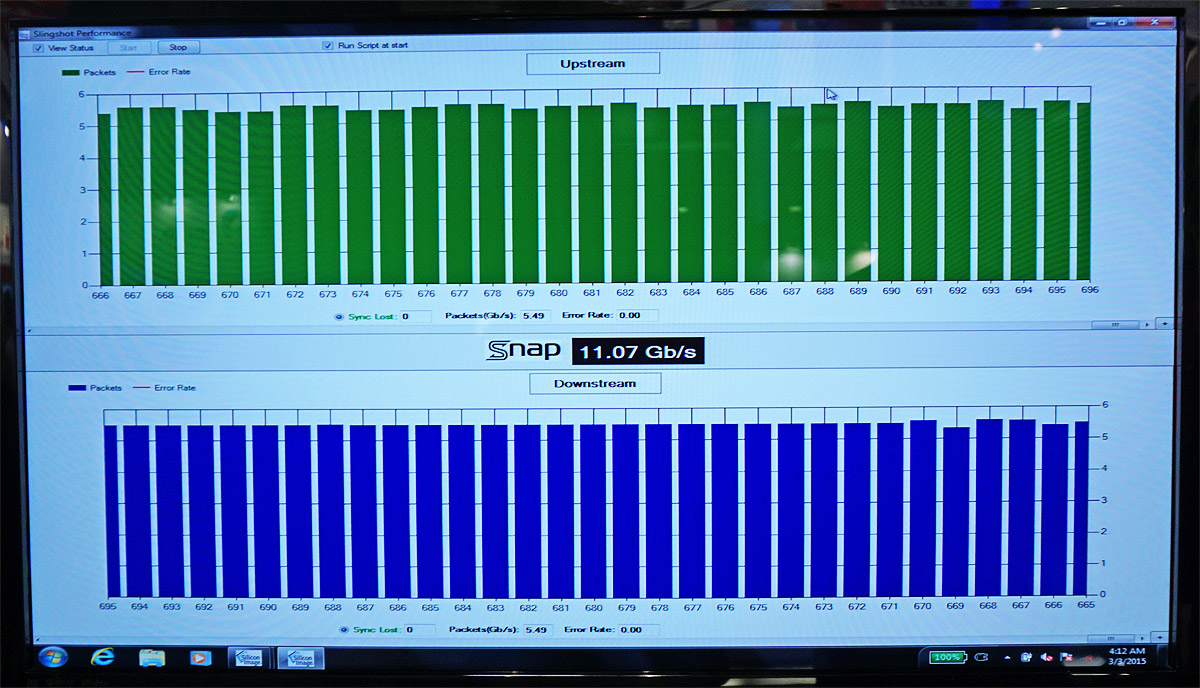
Combined with wireless charging, Snap could help eliminate USB ports from mobile devices, providing several benefits. First, it gives OEMs more freedom to reduce thickness or improve aesthetics when designing products. Implementing dust and water resistance also becomes easier and more foolproof with one less hole to plug. There's also the potential for higher-speed data transfers, depending on the supported protocol and the connecting bus.
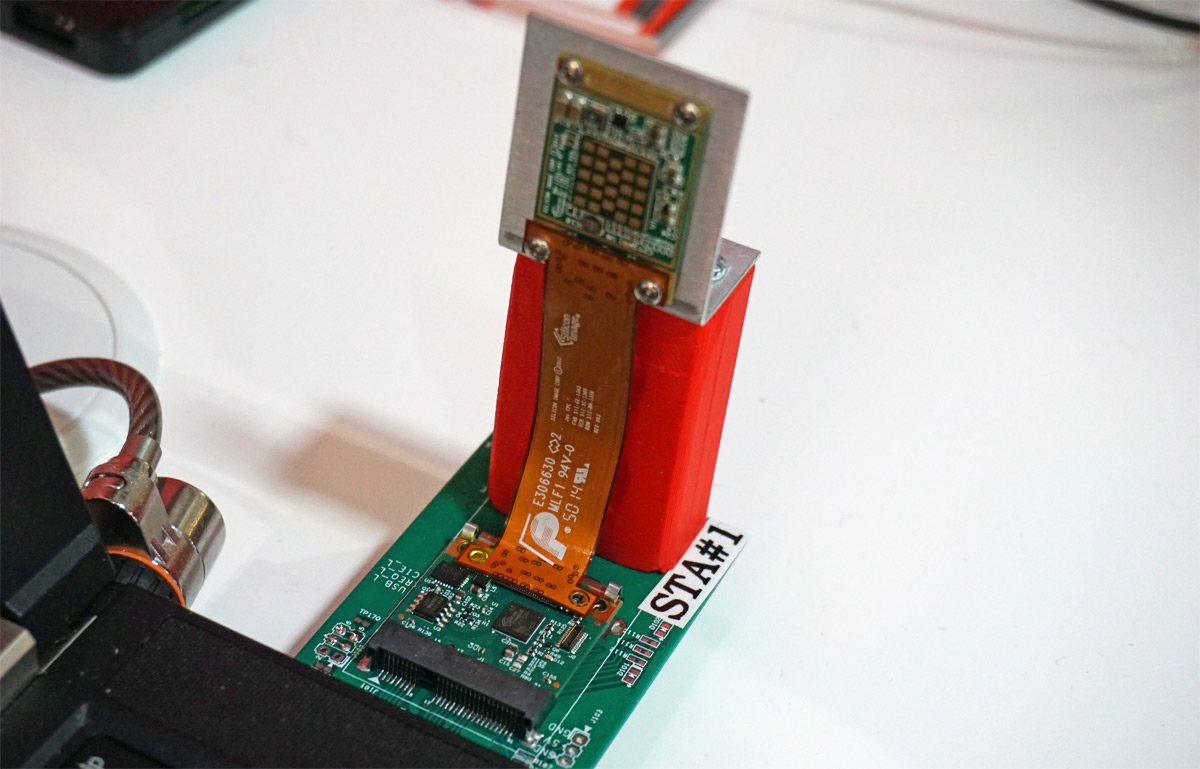
Although SiBEAM's Snap technology is limited to scenarios that involve physical contact with a receiving device like a docking station or pad, another 60 GHz technology, 802.11ad or WiGig, extends cable-free connections to anywhere within the same room. Unlike previous Wi-Fi standards that superseded those that came before it, WiGig will work alongside 802.11ac to offer high-speed local transmissions up to 7 Gb/s. There are several vendors, including SiBEAM, currently offering WiGig chipsets.
With the proliferation of wireless technology and ever increasing speeds, cables and connectors could soon be a thing of the past.
Follow us @tomshardware, on Facebook and on Google+.
Stay On the Cutting Edge: Get the Tom's Hardware Newsletter
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
-
TechyInAZ Nice idea, however I don't like the idea of having LOT more radio waves going thru my head.Reply -
warmon6 you've must of missed the "1 cm range" part for the tech this article was talking about.Reply
Shouldn't be going though your head if you had it sitting on a table or something like that (unless your placing it on your head.... then you might want to reconsider where your placing your phone at...) -
zodiacfml 1cm?! that sounds terrible versus WiGig.Reply
Wireless charging renders this less useful as low power advantage will be negligible.
Probably useful for specialized use in industries which I have no idea yet.
-
Ayu Natsume 1cm is good for NFC-like uses -- you don't want to pass around your ehem files to another nearby laptop eh. That SiBeam flashdrive shouldn't randomly connect to another device just because it got within range -- remember, its vouching on physical security just like the wired bus its supplementing.Reply
Its supposed to act like a 'wireless wired' connection -- the devices are fooled into thinking they are connected physically but IRL its wireless.
I'd like something like this. Think about just throwing your flashdrives and harddrives and cellphones and USB hardware key dongles and whatnot into a basket -- no need to even waste your time connecting them! I mean, this technically supercedes USB Type C's reversible connector and everything by not even having to plug anything in (except perhaps adapters.) Its similar to the old MS Surface's (the table top computer) ability to use phones that are put on top of it. The phones would act like as if they were connected -- in SiBeam's case, virtually physical.