Zen 5-based Threadripper 9000 CPU shipping manifest hints at imminent launch
New 24-core SKU has surfaced.

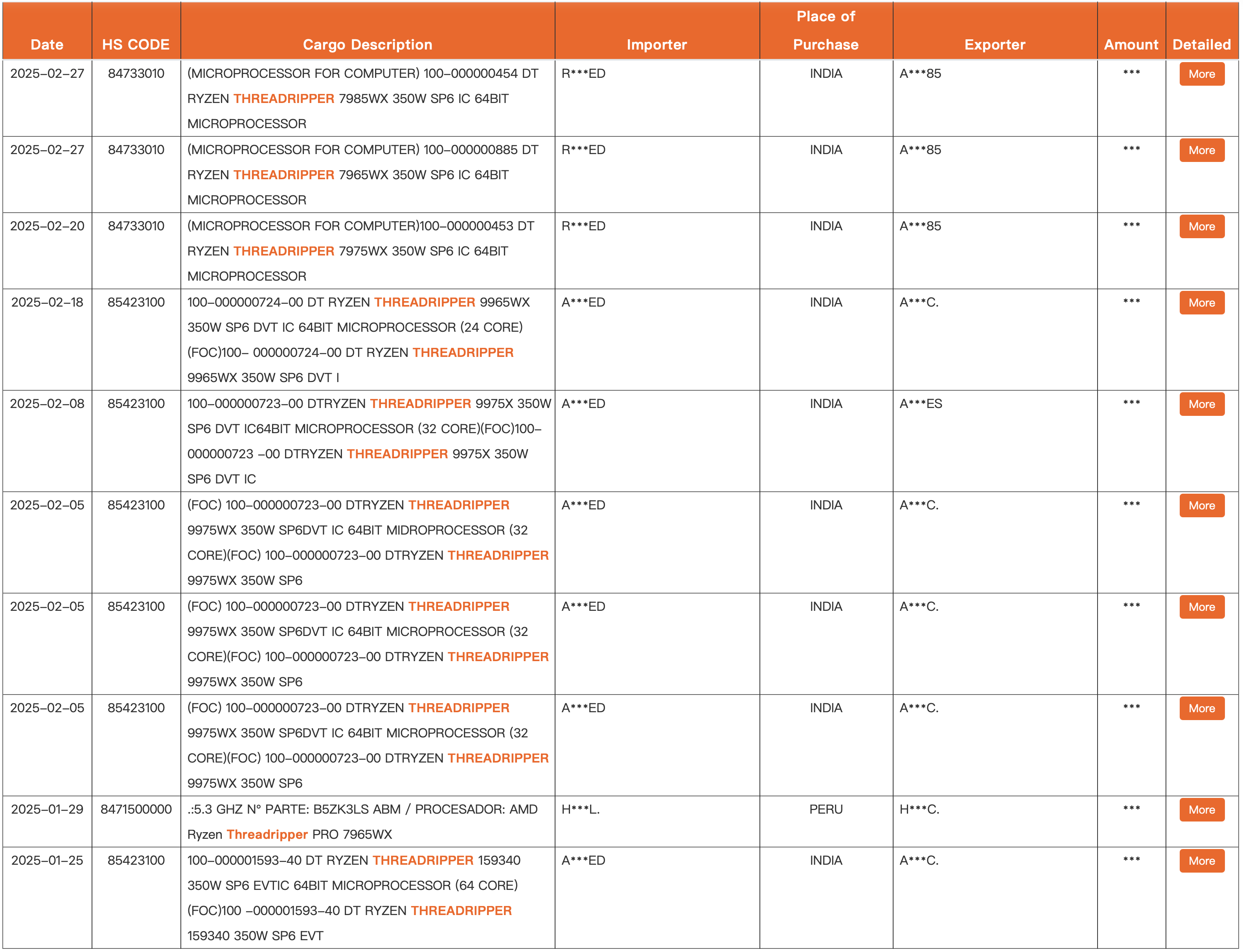
As the launch of AMD's Zen 5-based Ryzen Threadripper Pro 9000-series processors, codenamed Shimada Peak, is getting closer, more of these CPUs are spotted in various databases and shipment manifests. This week, blogger Everest noticed 24-core and 32-core Ryzen Threadripper Pro 9000-series processors in shipping manifests in the Global Trade Data and Customs Database. This does not mean that these units are set to hit the market shortly, but it means that someone is testing CPUs with appropriate names.
The processors in question are AMD's upcoming Ryzen Threadripper Pro 9975WX with 32 cores and Ryzen Threadripper 9965WX with 24 cores. Both CPUs feature a thermal design power of 350W, which aligns with the TDP of AMD's current-generation Ryzen Threadripper 7000-series CPUs. The same TDP will ensure the drop-in compatibility of AMD's Threadripper Pro 9000-series processors with existing platforms with appropriate firmware to support Zen 5-based CPUs.
Keep in mind that the information in shipping manifests is unofficial. However, observers have spotted three out of five or six Ryzen Threadripper Pro 9000-series CPUs in various shipping manifests. AMD still has to send its flagship Ryzen Threadripper 9995WX processor with 96 cores and entry-level Ryzen Threadripper 9955WX with 16 cores to one of its overseas offices for testing so that we could, to some degree, confirm the lineup, which could look as follows:
Ryzen Threadripper 9000 CPU Specifications*
Processor | Cores | TDP (W) | Socket | Product ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Ryzen Threadripper 9995WX | 96 | 350 | SP6 | ? |
Ryzen Threadripper 9985WX | 64 | 350 | SP6 | 100-000001593-40 |
Ryzen Threadripper 9975WX | 32 | 350 | SP6 | 100-000000723-00 |
Ryzen Threadripper 9965WX | 24 | 350 | SP6 | 100-000000724-00 |
Ryzen Threadripper 9955WX | 16 | 350 | SP6 | ? |
*Specifications are unconfirmed.
AMD's Ryzen Threadripper Pro 9000-series family is expected to feature five CPUs with 16, 24, 32, 64, and 96 cores relying on the Zen 5 microarchitecture. As AMD's Zen 5 core complex die (CCD) packs eight cores with 32 MB of L3 cache, this means that a 16-core Threadripper Pro 9000-series CPU will use two compute dies, a 32-core version will use four CCDs, a 64-core variant will come with eight CCDs, and a 96-core one will house 12 core complex dies and 384 MB of L3 cache. T
These values nearly match the current Threadripper 7000-series generation and suggest no changes to the cache structure. However, AMD may omit a 12-core version this time, at least according to rumors.
Regarding compatibility, the Ryzen Threadripper Pro 9000-series processors use an LGA-4844 packaging called 'SP6' in shipment manifests, which is not technically correct. While AMD's SP6 and sTR5 sockets are physically identical in dimension and the number of pins, they are not electrically compatible, meaning processors designed for one socket cannot operate in the other. AMD's Ryzen Threadripper Pro 9000-series will continue to use the socket sTR5.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.

Anton Shilov is a contributing writer at Tom’s Hardware. Over the past couple of decades, he has covered everything from CPUs and GPUs to supercomputers and from modern process technologies and latest fab tools to high-tech industry trends.
-
newtechldtech I dont get it , how on earth the 16 cores Threadripper has the same TDP of the 96 cores one ? and why 350W ??? The 16 cores Ryzen is only 170W ?Reply -
Notton There are many inconsistencies in the shipping manifest, so I'll assume the 350W is incorrect as well.Reply -
Neilbob All Threadripper models have always had the same TDP, regardless of core count. I'm pretty sure there is some technical reason for that to be the case, but I can't be bothered to search for it.Reply -
emike09 Reply
Probably a much higher base and boost clock. Or the data is wrong.newtechldtech said:I dont get it , how on earth the 16 cores Threadripper has the same TDP of the 96 cores one ? and why 350W ??? The 16 cores Ryzen is only 170W ? -
derekullo Reply
https://www.amd.com/en/products/processors/workstations/ryzen-threadripper.html#specificationsnewtechldtech said:I dont get it , how on earth the 16 cores Threadripper has the same TDP of the 96 cores one ? and why 350W ??? The 16 cores Ryzen is only 170W ?
Threadripper 7000 series, but you get the picture.
Just for comparison ...
https://www.amd.com/en/partner/articles/amd-ryzen-7000-series-desktop-processors.html
CPUCoresThreadsBoost ClockBase ClockCPU CoolerTDPAMD Ryzen™ Threadripper™ PRO 7945WX1224Up to 5.3 GHz4.7 GHzNot Included350WAMD Ryzen™ 9 7900X1224Up to 5.6 GHz4.7 GHzNot Included 170W -
usertests I wouldn't worry about the TDP much, look at how much it pulls in reviews once it's out.Reply
Or don't look at all since most people aren't going to be buying into the Threadripper platform.
I doubt a 16-core could pull much more than a 9950X though.
https://www.tomshardware.com/pc-components/cpus/amd-ryzen-9-9950x-cpu-review/4 -
The Historical Fidelity Reply
TDP stands for “thermal design power” and is more a description of how much power-derived heat can be dissipated by the package (the actual term references the amount of heat one can expect to need to dissipate during normal stock settings usage and is a helpful figure when determining the minimum performance cooling solution to use). Since the threadripper package size is massive vs consumer desktop parts, the heat spreader used allows equally massive cold plate coolers to efficiently remove heat from the package (IE pretty much all threadripper coolers are rated for 350 watts simply due to size plus the low volume nature of threadripper does not make it economical to make multiple performance levels of cooler when the majority of threadripper sales are the 64+ core models) .newtechldtech said:I dont get it , how on earth the 16 cores Threadripper has the same TDP of the 96 cores one ? and why 350W ??? The 16 cores Ryzen is only 170W ?
A real life example of TDP vs power usage is Intel’s flagship desktop CPUs. Looking at the Core i7-14900k, the TDP is 125 watts, but the power usage at its rated maximum boost frequency is 253 watts and Intel limits the amount of time the processor can pull that much power due to thermal runaway that would occur if a 125 watt TDP rated cooler is used. Enthusiasts with high end CPU coolers can run the CPU at 253 watts indefinitely but Intel does not consider that exception to rate the 14900k at 253 watt TDP because the majority of their customers (Dell and other system builders) do not use such high end coolers in their products. -
tamalero Reply
Or they are using all defective CCX.. aka with only 2 or 1 cores per CCX lol.emike09 said:Probably a much higher base and boost clock. Or the data is wrong. -
blkspade Reply
You are technically on the right path. Threadripper uses more CCDs than Ryzen for the same core count, with disabled cores. That facilitates full performance of the memory controller, which is also bigger than Ryzen. The entire IO die is also much larger to accommodate all the PCI-e lanes. All of that equals more power going into the package compared to Desktop Ryzen.tamalero said:Or they are using all defective CCX.. aka with only 2 or 1 cores per CCX lol.
The 9950x3D takes more power than the 9800x3D in gaming loads just because the extra die is present, even if it's not doing the work. With TR you could have each die hitting higher max clocks at full load than a 9950X, because it has so much more area to dissipate heat.