Intel's 45 nm Penryn CPU: 4 GHz Air Cooled
Overclocking V - 4 GHz At FSB 1600
To squeeze the maximum performance out of our engineering sample, we also benchmarked at 4 GHz with a front-side bus running at 400 MHZ (1600 QDR). For this test, we set the multiplier to 10x.
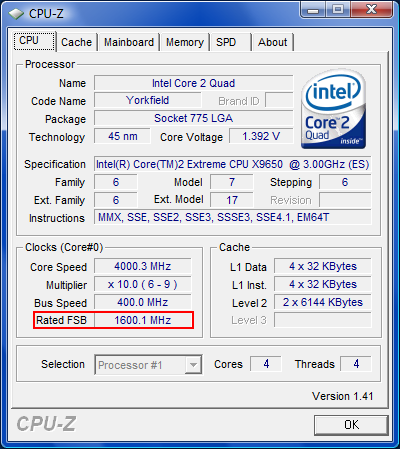
With the CPU running with these parameters, we first tested its stability using Prime95.
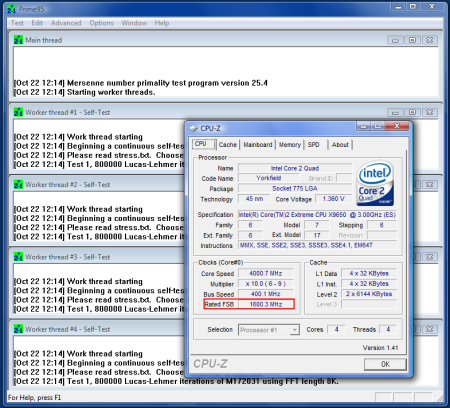
We succeeded at benching the QX9650 at 4.0 GHz with FSB 1600.
During our overclocking tests, we saw that the new 45 nm generation has a lot more overclocking potential, and the threshold between stable and unstable operation is a good deal wider. Where CPUs of the 65 nm generation simply wouldn't boot if the frequency was set too high, our 45 nm sample was at least able to load the operating system. This overclocking behavior is similar to that of the Northwood and Prescott processors of the Netburst microarchitecture. Even at high clock speeds, you should always at least be able to boot into your OS.
After our initial batch of tests, we can corroborate Intel's claim that the 45 nm design was created with high clock speeds in mind. It is entirely possible that the chipmaker will release models running at stock frequencies of 3.33 GHz and 3.66 GHz. Even 3.83 GHz is an option if that model used a standardized 400 MHz FSB (1600 QDR) or a half-step multiplier.
We'll take a look at power consumption and how it changes at higher clock speeds later on in this article, allowing us to cement our findings.
Stay On the Cutting Edge: Get the Tom's Hardware Newsletter
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Overclocking V - 4 GHz At FSB 1600
Prev Page Overclocking IV - 4 GHz At Very High Voltage Next Page Overclocking - Up To 19% More PerformanceTom's Hardware's dedicated news crew consists of both freelancers and staff with decades of experience reporting on the latest developments in CPUs, GPUs, super computing, Raspberry Pis and more.
